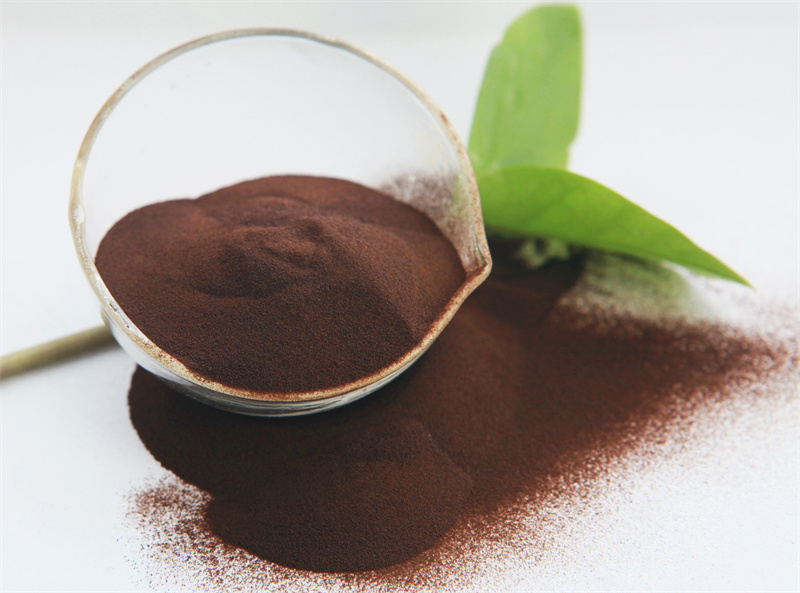
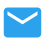
The basic component of sodium lignosulfonate is benzyl propane derivative. The sulfonic acid group determines that it has good water solubility, but it is insoluble in ethanol, acetone and other organic solvents. Typical softwood lignosulfonate can be expressed by the following chemical formula C9H8.5O2.5 (OCH3) 0.55 (SO3H) 0.4.
The structural characteristics and molecular weight distribution of lignosulfonate determine that it is different from other synthetic surfactants in many aspects. It has the following surface physical and chemical properties:
1.The surface active lignosulfonate molecule has many hydrophilic groups and no linear alkyl chain, so its oil solubility is very weak, its hydrophilicity is very strong, and its hydrophobic skeleton is spherical, and it can not have a neat phase interface arrangement like ordinary low molecular surfactants. Therefore, although it can reduce the surface tension of the solution, it has little control over the surface tension and will not form micelles.
2.The viscosity of the slurry can be reduced by adding a small amount of lignosulfonate into the viscous slurry through adsorption and dispersion; When added to the thinner suspension, the settling speed of suspended particles can be reduced. This is because lignosulfonate has strong hydrophilicity and electronegativity. It forms anionic groups in aqueous solution. When it is adsorbed on various organic or inorganic particles, the particles maintain a stable dispersion state due to the mutual repulsion between anionic groups. Some studies also show that the adsorption and dispersion of lignosulfonate are caused by the electrostatic repulsion force and the lubrication of tiny bubbles, The lubrication of micro bubbles is the main reason for its dispersion: the dispersion effect of lignosulfonate varies with its molecular weight and suspension system. Generally, fractions with molecular weight ranging from 5000 to 40,000 have better dispersion effect.
3.chelation lignosulfonate contains more phenol hydroxyl, alcohol hydroxyl, carboxyl and carbonyl groups, in which the un shared electron pairs on the oxygen atom can form coordination bonds with metal ions, resulting in chelation, forming metal chelates of lignin, thus having new characteristics. For example, chelation of lignosulfonate with iron ion, chromium ion, etc. can be used to prepare oil drilling mud thinner, and chelation also makes it have certain corrosion and scale inhibition effects, which can be used as water treatment agent.
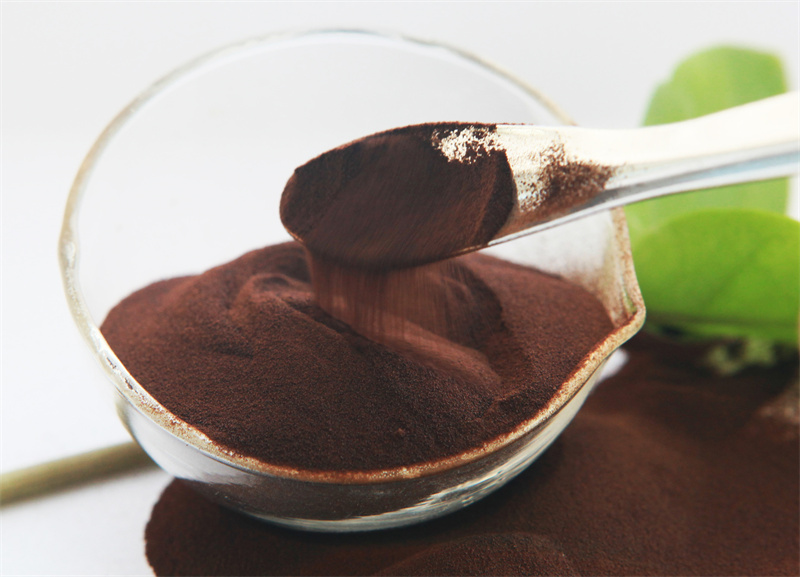

4.The bonding function is in natural plants. Like an adhesive, lignin is distributed around the fiber and between small fibers inside the fiber, inlaid with fibers and small fibers, making it a strong skeleton structure. The reason why trees can not fall down for tens of meters or even hundreds of meters is because of the adhesion of lignin. Lignosulfonate separated from black liquor can be modified to restore the original adhesive force, and the sugar and its derivatives in the waste liquor can help to enhance their adhesive force through mutual synergistic effect.
5.Foaming performance The foaming performance of lignosulfonate is similar to that of general polymer surfactants, which has the characteristics of low foaming capacity, but good stability of foam, and the foaming performance of lignosulfonate will have a certain impact on its application performance. For example, when it is used as a concrete water reducer, on the one hand, due to the lubrication of bubbles generated by lignosulfonate, the fluidity of concrete will increase and the workability will become better; On the other hand, the foaming property will increase the air entrainment and reduce the strength of concrete. When used as air entraining water reducing agent, it is beneficial to improve the frost resistance and durability of concrete.
Post time: May-08-2023