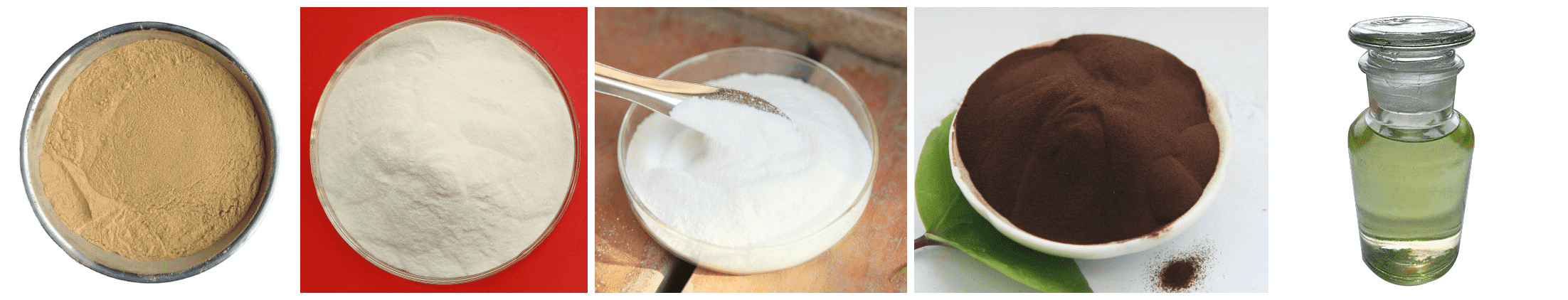
Classification of concrete admixtures:
1. Admixtures for improving the rheological properties of concrete mixtures, including various water reducers, air-entraining agents and pumping agents.
2. Admixtures for adjusting the setting time and hardening properties of concrete, including retarders, early-strength agents and accelerators.
3. Admixtures for improving the durability of concrete, including air-entraining agents, waterproofing agents and rust inhibitors, etc.
4. Admixtures to improve other properties of concrete, including air-entraining agents, expansion agents, antifreeze agents, colorants, waterproofing agents and pumping agents, etc.

Water reducer:
Water reducing agent refers to an admixture that can keep the workability of concrete unchanged and significantly reduce its mixing water consumption. Since the water reducing agent is added to the mixing house, if the unit water consumption is not changed, its workability can be significantly improved, so the water reducing agent is also called a plasticizer.
1. The mechanism of action of the water reducing agent After the cement is mixed with water, the cement particles will attract each other and form many flocs in the water. In the floc structure, a lot of mixing water is wrapped, so that these water cannot play the role of increasing the fluidity of the slurry. When the water-reducing agent is added, the water-reducing agent can disintegrate these flocculent structures and liberate the encapsulated free water, thereby improving the fluidity of the mixture. At this time, if the workability of the original concrete still needs to be kept unchanged, the mixing water can be significantly reduced and the water reducing effect can be achieved, so it is called a water reducing agent.
If the strength remains unchanged, the amount of cement can be reduced while reducing water to achieve the purpose of saving cement.
2. The technical and economic effects of using water reducing agent have the following technical and economic effects
a. The amount of mixing water can be reduced by 5~25% or more when the workability remains unchanged and the amount of cement is not reduced. Since the water-cement ratio is reduced by reducing the amount of mixing water, the strength can be increased by 15-20%, especially the early strength is improved more significantly.
b. Under the condition of keeping the original mix ratio unchanged, the slump of the mixture can be greatly increased (100~200mm can be increased), making it convenient for construction and meeting the requirements of pumping concrete construction.

c. If the strength and workability are maintained, the cement can be saved by 10~20%.
d. Due to the reduction of the amount of mixing water, the bleeding and segregation of the mixture can be improved, which can improve the frost resistance and impermeability of concrete. Therefore, the durability of the concrete used will be improved.
3. Currently commonly used water reducers
Water reducing agents mainly include lignin series, naphthalene series, resin series, molasses series and humic series, etc. Each type can be divided into ordinary water reducing agent, high-efficiency water reducing agent, early strength water reducing agent, retarder according to the main function. Water reducing agent, air-entraining water reducing agent, etc.
Post time: Feb-18-2022